The Complete Guide to Mobile Device Lifecycle Management
In today’s fast-paced tech landscape, mobile devices play a critical role in both consumer and enterprise operations. For businesses handling large volumes of devices, managing these assets efficiently isn’t just about tracking inventory—it’s about optimizing the entire device lifecycle to improve operational efficiency, compliance, and customer satisfaction.
This is where mobile device lifecycle management (MDLM) comes into play. Unlike traditional Mobile Device Management (MDM), which focuses primarily on security and IT administration, lifecycle management covers every stage of a device’s journey, from post-purchase use to resale. By implementing a comprehensive lifecycle strategy, businesses can protect data, maximize device value, and create a seamless experience for end-users.
What is Mobile Device Lifecycle Management?
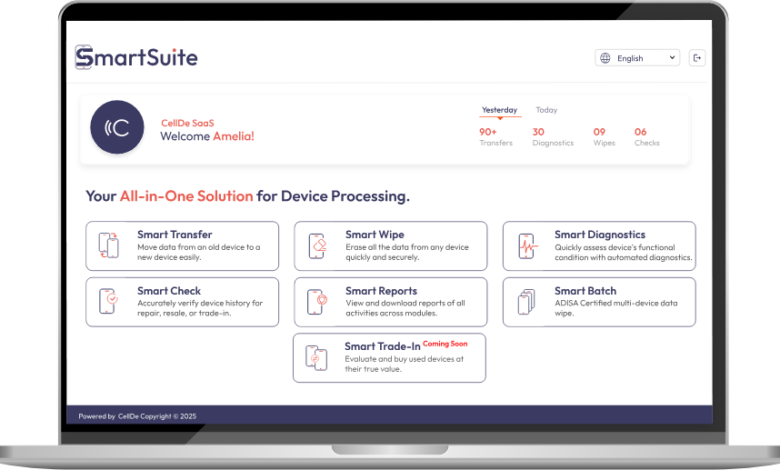
Mobile device lifecycle management is the process of overseeing a device from the moment it is purchased until its final stage—whether that’s resale, trade-in, or safe disposal. It goes beyond standard IT administration by addressing diagnostics, data transfer, performance checks, secure data erasure, and bulk processing.
This holistic approach ensures that devices are not only functional but also optimized for resale or trade-in value. It also supports operational efficiency by reducing downtime, minimizing errors, and ensuring compliance with data security regulations.
Businesses that embrace lifecycle management gain better control over inventory, can plan maintenance and replacements proactively, and provide a higher-quality experience to their customers.
Key Stages of Device Lifecycle Management
A mobile device passes through several key stages, each critical for maintaining its performance, security, and value. Understanding these stages allows businesses to implement processes that protect data and optimize operations.
1. Post-Purchase Setup
After a device is purchased, it must be configured correctly for immediate use. This stage includes:
- Initial software setup and updates
- Configuration of security and connectivity settings
- Activation of essential applications or enterprise profiles
For businesses offering devices to employees or customers, ensuring a smooth setup minimizes troubleshooting needs and reduces dissatisfaction. Automated setup tools can streamline this process, especially when managing bulk devices.
2. Device Diagnostics and Health Checks
Before devices are sold, resold, or traded in, their health must be evaluated. Diagnostics can include:
- Battery health and charging efficiency
- Storage availability and integrity
- Network and connectivity performance
- Software functionality and update status
Automated diagnostic software helps businesses identify issues early, allowing repairs or adjustments before devices leave the organization. This not only protects resale value but also ensures that customers receive devices in excellent working condition.
3. Data Transfer and Migration
Data transfer is a critical consideration for customers switching devices, particularly between platforms such as Android and iPhone. Key elements of this stage include:
- Secure migration of contacts, messages, photos, and apps
- Ensuring compatibility across operating systems
- Minimizing data loss or corruption
Businesses can provide a smoother customer experience by implementing reliable data transfer tools. This reduces the risk of frustration, lost information, or negative reviews, and enhances customer trust.
4. Secure Data Erasure
Before a device is resold, traded in, or recycled, it must undergo secure data erasure. Proper wiping is essential to:
- Protect sensitive personal or corporate data
- Maintain regulatory compliance
- Reduce liability from potential data breaches
Certified wiping processes, such as those adhering to recognized industry standards, ensure that data is completely removed while maintaining the device’s functionality. Businesses that neglect secure erasure risk reputational damage and legal consequences.
5. Trade-In, Resale, and Reporting
Devices ready for resale or trade-in must go through verification, testing, and processing. Key considerations include:
- Accurate device valuation based on diagnostics and condition
- Bulk processing of multiple devices efficiently
- Comprehensive reporting for inventory management and compliance
A structured workflow ensures that devices are handled consistently and fairly, improving operational efficiency and transparency. Businesses can also leverage reporting to monitor trends in device health, performance, and resale profitability.
See also: What to Include in a Grant Proposal for a Tech Company
Benefits of Lifecycle Management for Businesses
Implementing a comprehensive lifecycle management strategy delivers multiple benefits:
- Operational Efficiency: Automation and streamlined workflows reduce manual labor and errors, enabling faster processing of devices.
- Data Security: Secure data erasure protects sensitive customer and corporate information from breaches.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Fast setup, smooth data transfer, and reliable device performance improve satisfaction and loyalty.
- Sustainability and Compliance: Proper handling supports circular economy principles, reduces electronic waste, and meets regulatory requirements.
- Optimized Resale Value: Health checks and diagnostics ensure devices are resale-ready, maximizing returns on investment.
By focusing on the complete device lifecycle, businesses can transform a traditionally complex and resource-intensive process into a strategic advantage.
Lifecycle Management vs. Traditional MDM
It’s important to distinguish mobile device lifecycle management from traditional MDM solutions. While both are important, they serve different purposes:
Aspect
- Mobile Device Lifecycle Management
- Mobile Device Management (MDM)
Focus
- Entire device lifecycle
- IT security and configuration
Key Features
- Diagnostics, data transfer, secure wipe, trade-in, reporting
- Device settings, remote monitoring, policy enforcement
Beneficiaries
- Businesses and their customers
- IT teams and internal users
Goal
- Optimize operational efficiency and resale value
- Secure and manage devices for organizational use
While MDM primarily helps internal IT teams manage and secure devices, lifecycle management ensures that devices retain value, function properly, and support the business’s broader operational and customer-focused goals.
Trends and Challenges in Device Lifecycle Management
Businesses today face evolving challenges in device management, including:
- Increasing Device Volumes: Companies managing hundreds or thousands of devices need scalable solutions for diagnostics, setup, and resale.
- Cross-Platform Migration: Supporting multiple device types and operating systems requires sophisticated tools for data transfer and verification.
- Regulatory Compliance: Data privacy laws demand secure erasure practices to protect customer information.
- Sustainability Pressures: Organizations are under pressure to reduce e-waste and adopt circular economy principles.
Staying ahead of these trends requires a strategic approach, leveraging automation and advanced software solutions that handle diagnostics, data transfer, and secure wiping efficiently.
Best Practices for Effective Lifecycle Management
To ensure a successful lifecycle management program, businesses should consider the following best practices:
- Automate Wherever Possible: Use software tools to streamline diagnostics, performance checks, and data transfer.
- Implement Structured Workflows: Define processes for each stage of the device lifecycle to ensure consistency and efficiency.
- Focus on Security and Compliance: Always prioritize certified data wiping to protect sensitive information.
- Monitor Device Health: Track performance and battery health regularly to optimize resale or trade-in value.
- Adopt Circular Economy Principles: Incorporate trade-ins, refurbishment, and resale programs to reduce waste and maximize device value.
Conclusion
Mobile device lifecycle management is no longer optional for businesses managing multiple devices—it’s essential. By overseeing every stage of a device’s journey, companies can increase efficiency, protect sensitive data, enhance customer satisfaction, and support sustainability initiatives.
From setup and diagnostics to secure data wiping and resale, a well-planned lifecycle management strategy ensures that devices remain valuable and functional throughout their lifespan. For businesses handling trade-ins, upgrades, or resale programs, adopting these practices transforms device management from a complex challenge into a competitive advantage.
By prioritizing lifecycle management, businesses not only safeguard data and resources but also provide a seamless experience for their customers—helping them get the most out of every device, every time.